Industrial assets make the world go round. But these same assets, which help generate trillions of dollars of goods and services globally, have one common drawback: they deteriorate over time. That’s why companies whose profitability depends on those assets running smoothly allocate a substantial budget exclusively to maintenance. However, thanks to new technologies, these budgets have shrunk over time while providing improved productivity and, in turn, profitability.
Why is that? Let’s take a look at the different maintenance strategies companies use.
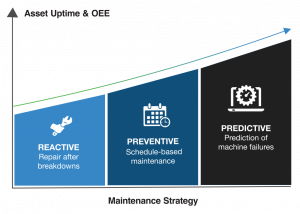
Preventive maintenance
This maintenance strategy, like all others, aims to catch failures and remediate faults before they impact the performance of the machinery. This is usually done by periodically checking and maintaining an asset based on the manufacturer’s recommendations.
As this strategy does not take into consideration an asset’s actual condition but rather the amount of time since its last inspection, there are a variety of drawbacks. These include:
- Maintaining assets that require no maintenance (over-maintaining)
- Results in high maintenance expenses with low effectiveness
- Increase asset failures as each time an asset is serviced and a part is replaced, a new risk of failure is introduced
- Missing a developing failure which causes a breakdown between maintenance checks
- Results in unplanned downtime, the need for expensive emergency repair and a large impact to the bottom line for every minute of lost productivity
- Poor visibility on the health of a company’s entire fleet of assets
- Lack of forecasting ability for CapEx and OpEx spend required to ensure business continuity
Condition-based maintenance
This maintenance strategy focuses on planning maintenance interventions based on the actual condition of the asset. Using sensors and asset data, operations teams monitor parameters such as temperature, humidity, or vibrations, and plan maintenance when a certain threshold is passed. A condition-based maintenance strategy:
- Reduces the amount of downtime to a maximum as problematic assets are identified and maintained
- Eliminates over-maintenance by letting healthy assets run
The main drawback is that most solutions on the market today require a heavy upfront investment (more on that below). But the company will benefit from a significant reduction in costs and improved productivity in the long-term.
Predictive maintenance
Predictive maintenance takes the same building blocks of condition-based monitoring and adds another layer: analytics. By using special algorithms, which ingest multiple asset-specific and system-level variables, operations teams can benefit from predicting future maintenance needs. This enables the most efficient type of maintenance, as insights like developing failures, risk of failure and time to failure enable teams to build the most efficient strategy with the highest ROI.
Although there are many benefits to implementing more advanced maintenance strategies, these can come with a significant upfront investment. Most solutions on the market provide significant benefits, but deploying these company-wide is often complex and expensive, with companies responsible for:
- Sourcing the building blocks of the solution and integrating hardware, software and analytics from different vendors
- Heavy-duty installation requiring specially trained personnel
- Hiring highly skilled maintenance engineers and data scientists to make sense of the data
Fortunately, advances in Artificial Intelligence and the Industrial Internet of Things have all but removed these barriers. Analytics can be embedded into the sensor, enabling each device to learn how to interpret the signals generated by each individual asset and alerting maintenance teams which assets need attention, when it will need it, and what kind of failure is developing. And advances in sensor technology and processing power means that many solutions on the market today are wireless, enabling easy and low-cost deployment at scale.
Today, it’s easier than ever for companies to implement and start benefitting from a predictive maintenance strategy.

